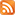Nothing kills the thrill of a freshly built or restructured website like your search engine rankings, traffic, and conversions plummeting the moment you push publish, yet it does happen. Of course, this is never on purpose and is typically the result of a lack of search engine optimization (SEO) skills or experience transferring a website. When sharing a website, most marketers and web developers overlook how search engines will respond and what the migration would mean for continued organic performance.
An SEO migration requires extensive study, planning, implementation, and monitoring to guarantee that your post-launch site retains and grows as much organic visibility as possible.
Understand that SEO migration aims to keep your website’s search engine rankings, traffic, and conversions intact. Therefore, you may preserve and improve your organic performance by undertaking a strict SEO website migration. Now, before we go too far ahead of ourselves, let’s start with what constitutes a successful SEO website migration and work our way down.
What Exactly is Website Migration?
A website migration involves significant URL, structure, content, UX, design, or platform changes. It might be anything from upgrading your website’s look to changing the URL structure or migrating your website to a new domain or content management system (CMS).
Your SEO services provider can help with all the technicalities involved in SEO website migration.
Website Migration Types
- Updating your website’s protocol from http to https
- Subdomain: Changing the address of your website from “www.yoursite.com” to “newsubdomain.yoursite.com”
- Changing the URL of your website from www.olddomain.com to www.newdomain.com
- Top-level domain: Change your website’s URL from.com to.org,.net, and so on, or vice versa.
- System for managing content: Transferring your website from one CMS to another, for example, from WordPress or Joomla to Umbraco CMS
- Redesign: Adjusting the website layout can vary from minor cosmetic tweaks to a complete website makeover with primary code and copy changes.
- Structural: Updating the architecture or structure of a website typically entails modifying either the user flow or the URL structure on which the website is constructed.
- Hybrid or combination migration: Utilizing a mix of the abovementioned migration types.
Does Migrating a Website Affect SEO?
When a website is migrated to a new domain, several factors can impact its search engine optimization (SEO) performance. To assess the potential impact, it is essential to consider several factors.
Firstly, the URL structure of the new website must be carefully planned to ensure that it maintains the same structure as the old website. Any changes to the URL structure can cause search engines to lose track of the pages on the website, leading to a significant drop in search engine rankings. It is important to set up proper redirects to ensure that users and search engines are redirected to the correct pages on the new website.
Secondly, the website’s content should be carefully reviewed and updated. For example, the content on the new website is significantly different from the old website, leading to a significant drop in search engine rankings. It is crucial to ensure the new website has the same content as the old website and that changes are made carefully. The website should be thoroughly tested before it is launched. This includes testing the website on different devices and browsers to ensure that it is accessible to all users, as well as trying the website’s load times to ensure that it loads quickly. A slow-loading website can negatively impact search engine rankings.
Also Read: Technical SEO Issues: Common Reasons Why Your Website is Not Ranking on SERPs
Why is SEO Important While Migrating a Website?
Over time, your site has gained organic exposure and equity, resulting in ranks for keywords and searches that your prospects and customers use to locate your website. Anytime you alter your URLs, content, or website in general, you change what search engines know about your website and the metrics they use to rank you. The objective of every website transfer is to minimize traffic losses as much as possible; doing a complete SEO migration guarantees that these losses do not occur.
What Happens if Your Website Migration Plan Does Not Incorporate SEO?
Simply, you risk losing search engine ranks, traffic and leads. We discovered that this prospect still needs an SEO migration plan after performing an SEO audit. Unfortunately, this is common – many firms relaunch their website out of sheer enthusiasm and frequently need to pay more attention to SEO.
How Long Should it Take to Migrate SEO?
The size of your website determines the length of an SEO migration, the amount of material being moved, and the pre-and post-audits required. A 100-page website will take much less time than a 1,000-page website, which will take much less time than a 50,000-page website, and so on. Some SEO migrations take a month to plan and carry out, while others take three months. Give yourself ample time to prepare, create a staging site, QA and audit, and execute. To be safe, we recommend allowing at least three months. Yet, it always depends on you and your team’s resources – ensure you address it thoroughly.
How Much Does it Cost to Migrate SEO?
The scope of the project determines the cost of SEO migration. It depends on the type of migration, the amount of material to migrate and create, the number of 301 redirects required, the total size of the website, auditing of the staging site, and implementation.
We recommend hiring an SEO professional or a business with prior experience moving a website with SEO in mind. It’s better to pay upfront for a proper SEO migration rather than choosing the “cheap” approach and having to circle back and solve errors repeatedly, potentially slowing — or worse, ruining — your organic performance.
SEO Migration Checklist
A thorough SEO migration plan that keeps migrations on track and schedule, resulting in greater search engine exposure is vital. Any of the checklist elements below can be used to ensure a successful migration, depending on the aim of the migration and how much time you have.
Choose an Appropriate Migration Date
Choose a launch date that is convenient for your team and website traffic. Then, consider all the effort required to create a suitable project timetable. Make sure you agree on project goals, redesign and approval timelines, development work, content production and updates, SEO migration duties, and day-of-launch job items, for example.
Choose a day and time when there is less traffic and interaction, preferably when your staff is all in the same office or space. As seductive as they seem, they should avoid weekends since they might cause coordination and communication challenges. Strive for an afternoon or early evening launch if debugging or unanticipated difficulties force you to work till the wee hours of the morning when there is little traffic.
Backup Your Website
Make a backup of your website so that if the launch goes wrong or does not go as planned, you may restore it to your previous site. Gather your marketing and web development teams to create a complete rollback strategy in case you need to return to the last website to iron out any bugs for a successful website transfer.
Make a Website for Staging
A staging website is a copy of your new website that people do not view; this is where you may test updates to your live site. By constructing a staging website, you offer your team enough time to assess how the material appears and operates and try and apply URL 301 redirects before going live. This eliminates the need to update URLs in internal links and sitemaps several times before and after launch.
Moving Website Sections
Consider “chunking” this action up in parts rather than moving everything at once if you’re relocating many properties, websites, or significant areas of an enterprise site for your website migration. This method makes the process more manageable and makes troubleshooting difficulties easier to spot before going live.
Do An Organic Health Check and A Backlink Audit on the New Domain
If you’re doing a domain migration, check the organic health of the domain you intend to migrate to. Has it ever been punished for spammy backlinks or content? Examine the website’s stats, such as Moz’s Domain Authority. This indicates challenges you could face in the long term.
Examine Your Website
Crawl your website with Moz Pro or ScreamingFrog to acquire a complete URL and content inventory. Not only will you use this to resolve bugs on your staging website, but you’ll also use it to map old URLs to new URLs in your 301 redirect map. This also aids in prioritizing which pieces of content to migrate and which internal links must be modified to reflect the new URL structure.
Emphasize the SEO Significance of Redirecting Website URLs
Crawl your site to collect all URLs on your domain and then rate which content on your website has the most search engine value using data from world-class analytics and SEO data sources such as Google Analytics, Majestic, SEMRush, and others.
This guarantees that high-priority URLs are included in your redirect file, and it may also assist you in determining what information needs to be updated, consolidated, or eliminated. Take the time to prioritize URLs on your website so that your most critical material performs well right away in your migration, and missing or outdated pieces of content may be added or updated to get the best SEO exposure possible.
Set up 301 redirects
Build and install a comprehensive 301 redirect map based on your SEO migration scoresheet. This ensures that the old website URLs properly redirect to their new URLs and that inside links redirect correctly, in case you missed them. Crawl this map before implementing to ensure that no redirects are broken and again after launch to ensure that everything redirects appropriately.
Simply create a column for your current/old URLs and another for their new URL equivalents. The file format depends entirely on your CMS and web developer preferences, so consult with them before creating a redirect file.
Also Read: Domain Authority 301 Rebranding
Update Internal Links
When you’ve updated your new URLs and have a list of what they will be, go to your test website and start upgrading internal links to avoid internal redirection or broken pages. ScreamingFrog can help you locate internal links, including their anchor text and the sites they’re on.
Make Customized 404 Page
You should design an appealing 404 page that users will view when they discover a broken link. This 404 page should direct them to your homepage or other pages on your site where they may locate what they’re looking for. A lack of 404 pages results in a blank page from which users cannot proceed, prompting them to abandon your site entirely.
Upgrade Google My Business and Bing Places
If you’re changing your domain, be sure to change your website’s link to the new domain in Google My Business (and other citation sites) and Bing Places. If you have many locations or offices, make sure to update the URL for each one. This is especially crucial to update if they have their own unique URLs (such as www.yourdomain.com/location). Remember that improving your Google My Business page is vital to your local SEO strategy. Google analyzes this information to authenticate your business and determine which queries to rank you for.
Refresh XML Sitemap
Create a new sitemap XML that may connect to your website (https://www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml) and publish it on Google Search Console.
This allows Google and other search engines to identify your critical service, product, or company information pages, allowing the new URLs to be indexed and returned in search results. Do this as soon as your site is live, because Google notices these changes quickly, and it’s critical to have them indexed and traffic flowing to them!
Notify Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools of the change in your domain name
Whenever you change your domain, use Google’s Search Console’s Change of Address tool. This informs Google that you have adjusted your domain and that it is now accessible via the new domain Address. Additionally, under Bing Webmaster Tools, utilize the Site Move Tool to alert Bing of your website relocation so that it may begin indexing your new URLs. You should do this as soon as your website becomes life.
Concentrate on Mobile-Friendliness
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning they look at your website’s mobile experience before indexing it, even on a desktop. Creating a mobile-friendly website that appears correctly across several devices and browsers guarantees that your website ranks appropriately. Google and other search engines like responsive design, so go responsive instead of creating a separate mobile website.
Do you need help determining whether your website is mobile-friendly? Google has a Mobile-Friendliness tool that evaluates your website and recommends improving the mobile experience, enhancing your organic exposure.
Migrate or Add Schema
In 2011, major search engines such as Google, Bing, Yandex, and Yahoo! developed a standard set of data markup options that webmasters may use to assist their crawlers in better comprehending the meaning of any content on a webpage. Schema.org is the name of this collaborative markup.
If you need Schema on your website, you should. While not a direct ranking criterion, studies show that it can assist in raising ranks and result in rich snippets, which leads to more excellent click-through rates.
In your transfer, include Schema or markup from your website. The schema may be migrated in a variety of ways, including:
- Copy/Paste Scheme into Body Text
Determine whether your Schema or structured data markup is HTML or Javascript-based first. Then, discuss your options with your web development team and how you can effectively use Schema utilizing these two ways. Following that, you copy or modify Schema to your chosen type and proceed with implementation, keeping URL, title tag, image, and other copy alterations in mind. - Use GTM to Populate Schema
You can also use GTM to insert Schema. However, we don’t encourage it because Google warns against using Google Tag Manager to create structured data markup. However, if you want to keep utilizing Schema in Google Tag Manager, here is the much needed help. - Use A Plugin to Implement Schema
Various plugins are available to assist you in integrating Schema on your website. We recommend researching plugins for the CMS you’re using or planning to use. Jooma and Umbraco provide a plethora of extensions to assist. Investigate how your web development company can integrate your CMS so content editors may add to your site.
If the solutions mentioned earlier don’t work, Google also provides the Structured Data Markup Highlighter to assist individuals who aren’t as comfortable with programming. Several prospects and clients have benefited greatly from it. We recommend that you test it out using Google Search Console.
Update your Robots.txt file
A robots.txt file, generally located at www.yoursite.com/robots.txt, notifies search engine crawlers which pages or files they may and cannot request from your site. Be sure to update your robots.txt file so Google understands which portions of your website to crawl and which to ignore. In addition, provide your new sitemap XML URL so that Google and other search engines can locate it.
Additionally, be sure to include your robots.txt URL in Google Search Console so that it is aware of its existence and may crawl it.
Update Your Backlinks
Without a doubt, your previous website has backlinks, especially if you have valuable location pages or documents. Check Search Console, Moz Link Explorer, Majestic, or any other backlink tool to discover which pages are accumulating backlinks. Next, contact the websites linked to your own and get the backlinks updated so that you may receive all of that backlink equity. This will take time; therefore, have someone maintain track of these backlinks, cover outreach, and annotate when a backlink is changed in Analytics.
Maintain Control of Your Previous Domain
Maintain management of your former domain so that you retain the domain name real estate and can verify that any hyperlinks referring to it are appropriately redirected. If you let rid of that domain, someone else can take it over and start a site, and you will lose your backlinks.
Instead, preserve it and continue accumulating all of the search engine equity you’ve generated for it over the years.
Do a QA and SEO audit before and after the launch.
Do an SEO audit before and after migrating and launching your website to ensure that all pages, content, links, tags, and mobile elements are present and correct. All SEO job items must be in place before you begin your migration and be correctly moved with your site afterward. To complete this audit, you must:
- Run a Crawl: Use ScreamingFrog to crawl your website quickly. Look for:
- Pages with errors (4xxs)
- Redirects (3xxs) (3xxs)
- Images that are broken
- Meta tags are missing.
- Content duplication
- There are no or incorrect canonical tags.
- Pages that have not been “noindexed.”
- Analyze Analytics: Verify that Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager are both appropriately installed and collecting data on your website. The simplest method to accomplish this is to use Google Analytics Real-Time Analytics report, which provides — you guessed it — real-time information to individuals who are now visiting your website.
- Take out your phone and navigate to your website to test it on mobile. First, ensure your website is responsive and renders correctly on mobile devices. Afterward, ensure that all layouts, designs, and functionality are in functioning order. Finally, use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to see if Google considers your site to be mobile-friendly and, if not, what you can do to comply.
- Verify That All Integrations Function: Verify that all your integrations function correctly. The tools you need to manage your website, in addition to Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager, include your CRM, marketing automation, customization, eCommerce, live chat, and other tools.
- Updating All Your Social Media Profiles: Check the links to your website on each social media profile to ensure they are current and accurate.
- Make Sure Bing Locations and Google My Business Are Updated: Verify new website addresses are included in Google My Business and Bing Places if required. In addition, it should update all pertinent information that the migration may have altered or impacted.
- Check For Broken Backlinks: You’ll have a good idea of which pages have backlinks before launch and can compare them with broken pages on your site after the launch crawl, but keep in mind that there are additional tools, such as the links report in Search Console and Majestic, that can help you find broken links. The hyperlinks you have access to can then be updated, or you can contact website owners and ask them to do so.
Also Read: The 15 Best Technical SEO Tools Every Webmaster Should Know!
A post-migration deployment requires several checks. First, be aware of every SEO and website performance component, especially the Google-recommended best practices. Although this post-migration review is essential, you should also periodically assess your website (at least monthly to quarterly).
Track Performance After Launch
This is more than just pressing “Go live” and walking away. First, ensure that the site is launched successfully, that no pages are damaged, and that the activities mentioned earlier have been carried out. Watch your Google Analytics throughout the next week to the month after that. Check your page performance across different devices and browsers, observe engagement metrics, and ensure that sites receive search traffic.
Beyond that, monitor the organic prominence of your keywords.
- Ranking Performance: Before the migration, your site was ranked for the keywords and searches people used to reach it; you’ll probably want to preserve those rankings so they may continue bringing people to your site. Be careful to compare your visibility performance for such keywords both before and after the launch using tools like Moz Pro and SEMRush. If they rise, fantastic; if they fall, you’ve got work to do.
- Users/Sessions of Organic Traffic: Use Google Analytics to look at your organic traffic. Examine your website’s essential pages, such as the homepage, service/product pages, and blog posts, to see whether traffic is dropping, holding steady, or rising following your move. This may be accomplished by comparing traffic before and after migrations and traffic from year to year. Next, look at the pages with the most swings in organic traffic. This will indicate whether certain pages require more optimization or whether those with traffic growth may be used as templates for other sites to achieve the same objectives.
- Problems with Google Search Console’s Site Crawl or Indexing: By this point, your website should have a Google Search Console profile created and configured. This is your best option for getting immediate information on how Google is indexing, crawling, and ranking your website. In addition, to keep track of any mistakes Google discovers on your website, often check Crawl Errors in Search Console. In particular, as you add material, check your Indexing Report to ensure URLs on your website are getting indexed and staying put.
To rapidly identify and add new redirects to your 301 redirect file, you should also pay attention to 404-page traffic in your Google Analytics post-launch. Also, by doing this, you may find any missing material you could have missed throughout your migration.
How to Use Google Analytics to Monitor 404 Pages
Create and optimize a 404 page to direct users to a page that informs them the page they are trying to access doesn’t exist. They have alternatives to either search for the material they were searching for or navigate to other pages on the website from the optimized 404 page. Create a 404 page with a page title initially to track 404 pages in Google Analytics.
- Start by selecting your Landing Page report from the Behavior reports’ Site Content section.
- Set the date in Analytics to reflect the passing of time since your website’s debut.
- Change the Google Analytics date range
- Choose “Page Title” as the secondary dimension.
- Create an advanced filter to look for “Page Titles that say “Page Not Found” or whatever the title of your 404 page is.
- Following that, you’ll receive a report containing every URL returning a 404.
- reports for 404 pages in Google Analytics
From here, you can provide your web development team with the URLs causing 404s so they can correctly 301 redirect them to live sites. This improves the user experience for visitors to your website and decreases broken pages, which makes it simpler for search engines to index.
Conclusion
A successful website transfer requires extensive study, planning, implementation, and measurement. It is a complex operation. In order to maintain and improve your organic exposure after launch, you must consider various factors. However, you’ll get the most visibility out of your SEO efforts throughout your site migration if you take the time to complete the activities mentioned above.
FAQs
What is a website migration in SEO?
A website migration refers to the process of moving a website from one domain or hosting platform to another. This can include changes to the website’s URL structure, content, design, and functionality.
Why is a website migration important for SEO?
Website migration can significantly impact a website’s search engine optimization (SEO) performance. If not executed properly, it can lead to a drop in search engine rankings and a loss of organic traffic. Therefore, it is essential to follow a checklist to ensure that the migration is done correctly.
What is the Ultimate SEO Website Migration Checklist?
The Ultimate SEO Website Migration Checklist is a comprehensive list of steps that should take to ensure a successful website migration without negatively impacting SEO performance.
What are the key elements of the Ultimate SEO Website Migration Checklist?
The key elements of the Ultimate SEO Website Migration Checklist include planning and preparation, website content and structure, redirects and domain setup, website testing, and monitoring and maintenance.
Why are planning and preparation important for website migration?
Planning and preparation are critical to the success of a website migration. This includes setting goals, identifying potential risks and challenges, and developing a detailed project plan. It is also essential to communicate the migration plan to all stakeholders to ensure everyone knows the timeline and expectations.
How can website content and structure impact SEO during a migration?
Website content and structure can significantly impact SEO during a migration. It is essential to maintain the same content and URL structure as much as possible to ensure that search engines can find and index the pages correctly. Any changes to the scope or structure should be made with careful consideration and a plan for redirecting old URLs to new ones.
What are redirects, and why are they essential during a migration?
Redirects are instructions that tell search engines and web browsers to transfer visitors from one URL to another. They are essential during migration to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct pages on the new website. In addition, proper redirect setup can help maintain search engine rankings and prevent a loss of organic traffic.
Why is website testing necessary during a migration?
Website testing is important during migration to ensure that the new website functions correctly and loads quickly on all devices and browsers. This can help prevent any negative impact on SEO due to slow page load times or broken links.
What is monitoring and maintenance of website migration?
Monitoring and maintenance refer to the ongoing process of tracking website performance and making updates and adjustments as needed. This includes monitoring search engine rankings, traffic, and user behavior to identify any issues that may arise after the migration. It is essential to promptly make any necessary updates or fixes to maintain SEO performance.