eCommerce website optimization requires knowing exactly what Google wants from your ecommerce store and making sure all of your technical needs are met. Thankfully, performing an ecommerce technical SEO audit is a great starting point for this process. An ecommerce technical SEO audit is a comprehensive review of your ecommerce website in order to identify any hidden issues that could prevent it from ranking well with search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo. This step-by-step guide should provide the simple tips and information necessary to ensure an ecommerce technical SEO audit goes smoothly without any hiccups or delays. From there you can start enjoying the rewards of increased ecommerce website traffic, higher conversion rates and increased online revenue.
Unfortunately, due to frequent updates and developments, even widely used platforms such as Shopify or WooCommerce can contain glitches and errors that harm your SEO. In such cases it is advisable that you use ecommerce SEO services from a reputed company that will detect any persistent technical issues and work to rectify them.
There is frequent confusion about the difference between eCommerce SEO and technical SEO for eCommerce sites. Technical SEO is fundamentally about correcting errors that prevent search engines from quickly understanding what your web page is about. It is one of the most effective ways to reap the full benefits of eCommerce SEO.
This could indicate that your site has broken links that lead to dead ends and wasted time when Google crawls it. It could also mean duplicate content, which causes search engines to become confused or any other technical SEO issues. So, here are the top things to watch out for when it comes to technical SEO for eCommerce.
What is a Technical SEO Audit?
A technical SEO audit is a process used to evaluate and analyze the technical aspects of a website that can impact its search engine rankings. This analysis covers technical elements such as page speed, usability, functionality, site structure, and security issues. Instead of viewing your site from the perspective of your customers, this process examines it from the perspective of Googlebot.
If you have thousands of product pages on your eCommerce site, you may not even know where the problems are, let alone how to fix them. Learning how to perform an ecommerce technical SEO audit will provide you with the information you need to ensure that your entire site is up and running smoothly.
It is critical to gain this perspective. It allows you to optimize your site, improve your SERP rankings, and give your users more value.
An audit is the first step in improving your technical SEO. It is also not a one-time thing; it should be done on a regular basis to ensure that no new issues are impeding your rankings. The more reliant you are on organic search traffic, the more audits you should conduct. Audits should also be performed after major site content or theme changes. This post will walk you through the most important things to look for.
Also Read: SEO Audit Pricing: How Much Does an SEO Audit Cost in 2025?
Conduct an eCommerce Technical SEO Audit

First and foremost, you should conduct a technical audit for SEO eCommerce. You will undoubtedly require an SEO tool for this step.
Paid Tools vs Free Tools
Many of the time consuming tasks can be made easier if you use a powerful SEO tool like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or SemRush. We have also included specific tools for each step so that you can cover all of your bases. You can also use a free tool like Google’s web.dev to get a comprehensive look at most of these factors, as well as recommendations for improving your site’s performance and rankings.
Also Read: Top 15 Ahrefs Alternatives: Free & Paid to Use in 2025
Use a Website Crawlers to Find Errors
You can use any website crawler to find potential technical errors that might impact the site SEO. When you enter your URL, it will scan the links, code, and images on your website. Then it provides a detailed summary, including any broken links, missing metadata, errors, and so on. Some of the most used website crawler tools are:
Ahrefs Broken Link Checker
Semrush Site Audit
Moz Pro
Screaming Frog
WooRank
When sifting through the results, keep the following in mind:
- Pages that contain 404 errors: That means the server was unable to retrieve any page content. AKA the page no longer exists and the URL is a broken link. Any 404 pages should be redirected to live pages with current, relevant content.
- URLs with HTTP codes: Any HTTP URLs that you have and are not working, and a technical eCommerce SEO audit will detect them. To ensure that all of your URLs are HTTPS, you must have an up-to-date, correct SSL certificate.
- Status of the XML sitemap: Every website includes an XML sitemap. When Google crawls your website and tries to deduce its meaning, it uses it as a map to help it navigate the pages. Every XML sitemap should be formatted as an XML document, adhere to the XML protocol, and include all of your site’s current web pages. The sitemap must then be submitted to Google Search Console.
- Duplicate content: Pages with duplicate meta data (titles, descriptions, headers, and so on) will be flagged. The information can then be updated to make it unique. The best eCommerce platform for SEO will include functionality to assist you in avoiding duplicate content.
Also Read: Best way to handle duplicate content in ecommerce site
- Meta information length: Meta descriptions and page titles should be 160 and 60 characters long, respectively. However, pixel width is a better way to look at it. Meta descriptions and meta titles should have pixel widths of less than 920px and 512px, respectively. SEMrush will display all of your pages with excessively long meta information.
- Pages that have 302 redirects: When a page is temporarily redirected to another page, a 302 redirect is used. However, most redirects are not temporary. Change any 302 redirects you have set up for permanent redirects to 301 redirects.
Once you have taken care of all these, you can proceed with the following steps.
Optimize page speed
The user experience is influenced by how quickly your web pages load. That is why Google considers clunky, slow web pages to be a negative. Go to Google PageSpeed Insights to test the speed of your website.
Once there, enter the URL of your website. After that, you will be given an overall page speed score, a breakdown of four important Core Web Vitals scores, and a list of ways to improve your scores.
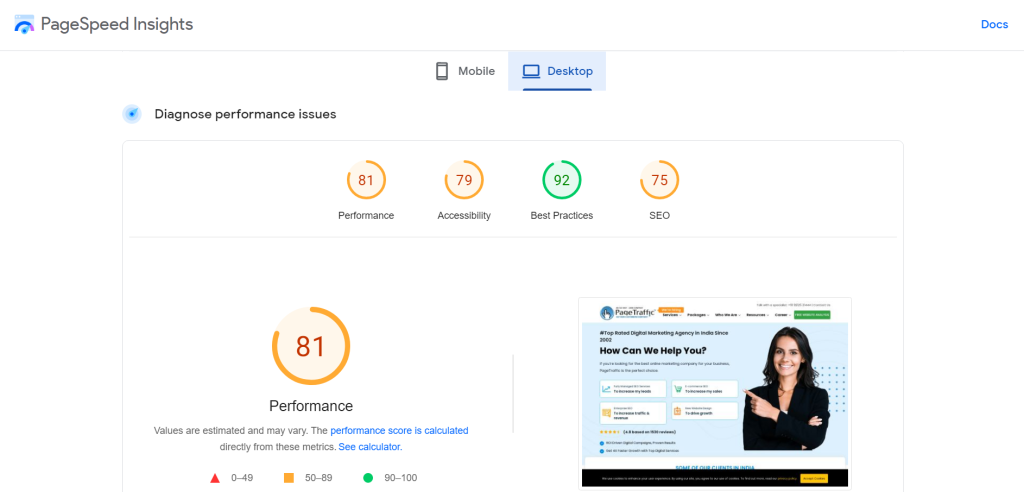
When using PageSpeed Insights, Google looks at four Core Web Vitals:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): FCP measures the time between when the page starts loading and when any part of the page’s content appears on the screen for the first time. Text, images, and non-white canvas or background elements are examples of content.
- First Input Delay (FID): FID is a metric for interactivity. It measures the time between when a user interacts with a page for the first time and when the page is able to process that interaction. It refers to how quickly a page can respond to clicks or other inputs after it begins loading.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): LCP is the amount of time it takes for the largest image or text block to be fully rendered on the screen.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS measures apparent stability. When you scroll down a web page, everything shifts because something loaded late? That is visual instability, and it creates a negative user experience. With a better CLS, less of this occurs.
All four of these have a direct impact on the user experience and are taken into account by Google when ranking pages. They contribute to your total page speed score, along with the Speed Index, Time to Interactive, and Total Blocking Time. It is critical to comprehend SEO terminology and how it can benefit your eCommerce site.
So, how do you ensure that these scores are adequate?
There are two options. The simplest solution is to use an eCommerce platform that is built for mobile and is optimized for page speed and user experience.
You can also do it on your own. PageSpeed Insights generates a hit list, which you can then send to a developer to make any necessary changes to your website.
Examine your website’s mobile version
Mobile traffic accounts for roughly half of all web traffic worldwide. That means that if your website isn’t designed to provide an optimal experience for 50% of users, your search rankings will suffer.
So, how do you ensure your site is mobile-friendly?
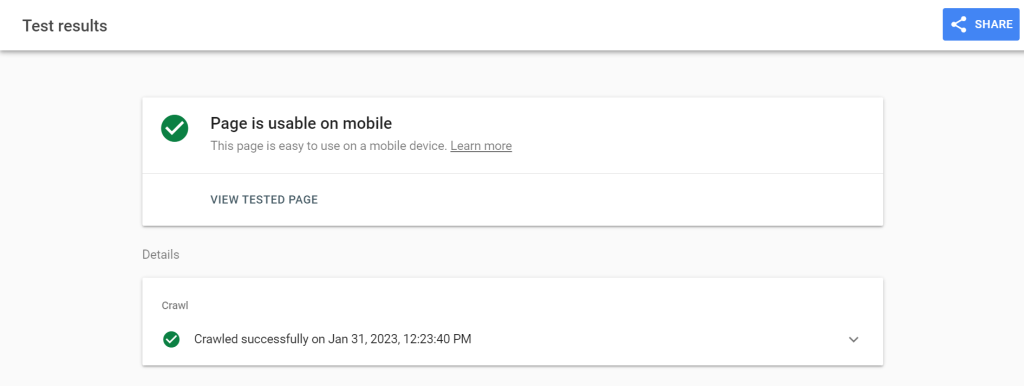
Again, the simplest solution is to use an online marketplace or platform designed for mobile responsiveness and optimal user experience at any screen size. You can also do it yourself. Actually, it’s not that difficult. Google has provided a mobile site test, Google’s Test My Site.
Enter your URL to get a list of ways to improve your site’s speed, personalization, and usability.
You should also strive for:
- Flexible text and image sizes ensure that your web page’s text and images remain legible and visible regardless of the size of the screen used to view it.
- A fluid grid layout, or a web page layout that resizes automatically based on the size of the screen used to view your web page.
- Modern content management systems, or the software used to create and publish web pages, are frequently mobile responsive. This is more of a problem with older web pages.
However, it is something that can always be improved, even if only slightly. And sometimes minor SEO victories make all the difference.
Analyze your sitemap
Without a sitemap, search engines will be unable to understand the structure of your eCommerce site and crawl all of your important pages. Most CMSs and eCommerce platforms will generate an XML sitemap for your eCommerce site automatically. Google Search Console can be used to check your sitemap for errors.
An XML sitemap is required for crawlability and indexation. It is designed specifically for search engines and instructs them on how to handle all of the information on your website. This way, the bots will know what to do and how to index without having to crawl your entire site (which they won’t do anyway due to limited crawl budgets).
Make sure your sitemap has been submitted to Google Search Console when it comes to best practises for sitemaps. After that, go over the coverage report. With this information, you’ll be able to correct any incorrect redirects, broken links, and missing pages.
Find and replace duplicate content
Identify and redirect any duplicate content on your site to the one you want search engines to index. You can use a tool like Siteliner to identify internal duplicate content on your website.
It is worth noting that duplicate content is no longer as detrimental to SEO results as it once was. Google has begun to recognise that certain types of eCommerce content are more likely than others to be duplicated. Previously, duplicate content could have resulted in a penalty; today, your duplicate content is more likely to compete with other sites that have taken the time to optimize their content to be unique.
Look for broken links
Broken links are literal dead ends for your customers as well as the Google crawler that reads your site. Locate and prune them.
The majority of ecommerce technical SEO audit tools will report broken links as 404 errors. 404 errors are browser errors that indicate that a page URL could not be located. Ahrefs provides a free Broken Link Checker to assist you in locating them.
Once you have compiled a list of broken links, consider whether the 404 error was caused by a technical issue or if it was intended (like when a product is discontinued). Broken links can be repaired with redirects or by restoring content to the affected page.
Check Security Issues
A straightforward test to begin. Simply enter the domain’s URL into a Google search to determine whether it is safe. Follow these domain iterations:
Domain.com
www.domain.com
HTTPS://domain.com
HTTPS://www.domain.com
If they all connect to the main domain and are secured, everything is fine.
This is yet another quick method to determine whether the domain is safe:
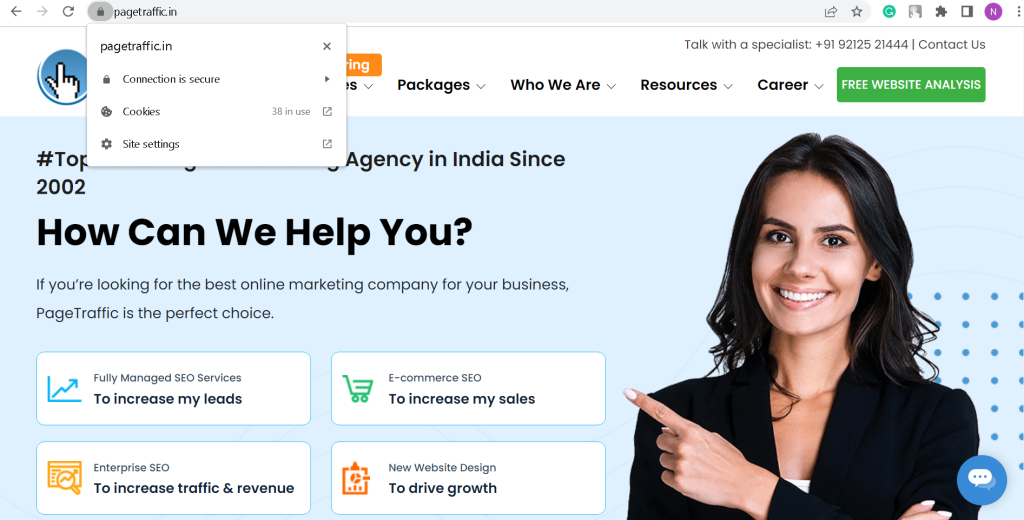
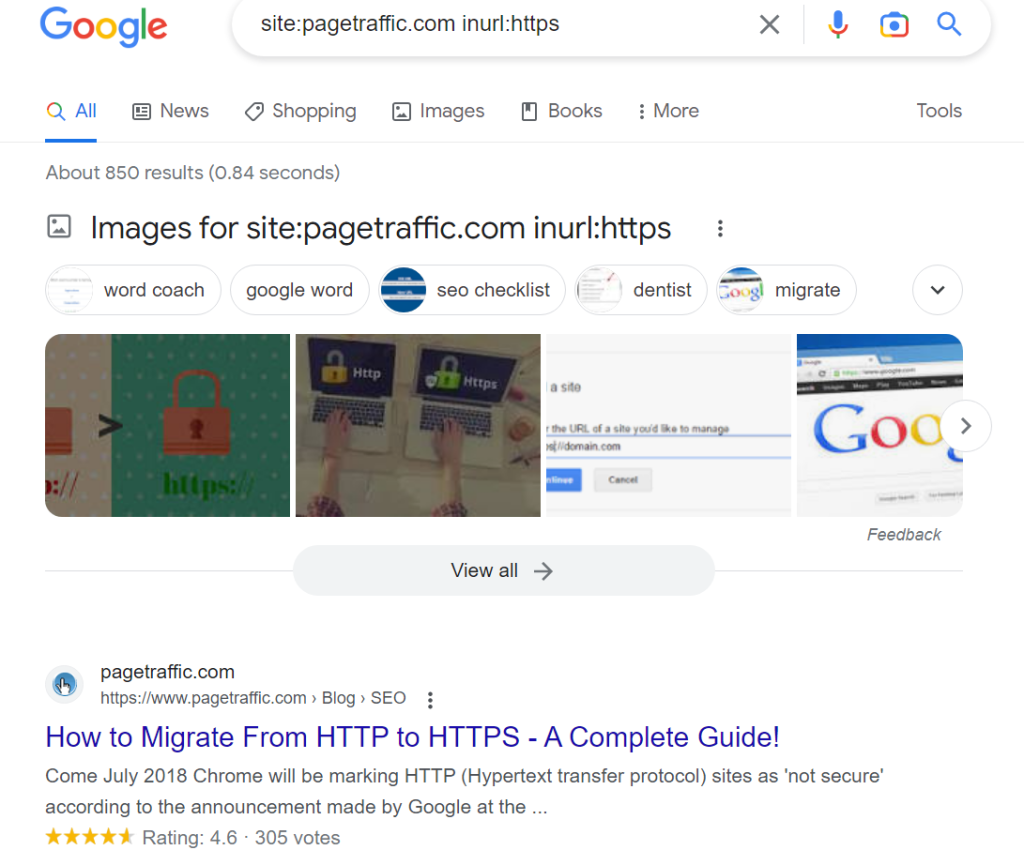
Perform a search on Google for: site: URL for domain.com: www;
If nothing appears, this indicates that the domain is safe.
Perform a search on Google for: site: URL for domain.com: https;
You are also doing well if a lot of pages appear.
Repair everything
The easy part is checking. You must now address all of the issues that were identified in steps 1-5. Fortunately, the majority of the tools at your disposal will provide recommendations for how to resolve the issues. Set a priority for them and begin working through them until they are completed.
Technical SEO audits will provide you with a wealth of information about what’s going on beneath the hood of your eCommerce site. After a thorough cleaning, it will be crawlable, indexable, and rankable, and will appear in Google search results.
How to Fix Common Technical SEO Issues On eCommerce Websites
Too Many Pages
Managing a website with a substantial number of pages can present significant challenges in terms of technical SEO. The task of creating unique content for each page becomes increasingly daunting as the page count grows. Additionally, with a higher number of pages, the likelihood of encountering issues related to duplicate content also rises.
Why It Happens
This issue is particularly common on ecommerce sites, especially those with a vast product inventory. The necessity for distinct product pages contributes to the accumulation of a large number of pages. Moreover, variations in the same product, such as different sizes, may result in each version having its own unique URL. This approach could potentially lead to an escalation in the overall page count of your ecommerce site.
How to Fix it
Identify pages that can be deleted or noindexed without affecting overall performance.
Based on our experience, a significant portion of an ecommerce site’s revenue, approximately 80%, is generated by just 20% of its products—a manifestation of the classic 80/20 principle. Surprisingly, nearly a quarter of ecommerce product pages showed no sales in the previous year.
Instead of expending effort on enhancing these underperforming pages, it is more beneficial to either remove them entirely, noindex them, or consolidate them into a unified “super page.”
Many ecommerce Content Management Systems (CMSs), including Shopify, facilitate the identification of products with no recent revenue. If they haven’t contributed to your earnings, consider placing them on a “maybe delete” list.
However, before proceeding with deletion, cross-reference Google Analytics to ensure that these pages aren’t generating any traffic.
Navigate to Google Analytics and focus on the landing pages section. If a page isn’t directing users to your site or contributing to revenue, it’s time to reconsider its relevance.
In some instances, these “deadweight” pages may comprise only 5-10% of your site, while in others, they may constitute 50% or more.
Once you’ve eliminated any unnecessary pages that may be causing issues, shift your attention to refining and improving the remaining pages.
Duplicate Content
Identifying pages that can be deleted or noindexed without affecting overall performance is the initial step.
Duplicate content poses a significant challenge in ecommerce SEO, often jeopardizing your site’s visibility in Google search results due to the impact of Google Panda. Adopting a targeted approach to ensuring unique content throughout all pages of your ecommerce site, along with implementing advanced SEO strategies like canonical tags, can effectively address these concerns.
Why It Occurs
Duplicate content on ecommerce platforms stems from various circumstances. Let’s delve into the three primary reasons.
Firstly, some websites create distinct URLs for each iteration of a product or category page. For instance, if your category menu layout results in unique URLs for each user selection, Google might index a substantial amount of duplicate content. This issue can also arise when multiple sizes or colors of the same product generate unique product page URLs.
The second common factor is boilerplate content, where a piece of text is duplicated across multiple pages. While using identical content on each page, such as a brief company introduction, is acceptable, surpassing 100+ words can prompt Google to categorize it as duplicate content.
Lastly, duplicated descriptions exacerbate the problem. This occurs when the same or highly similar content appears on several product or category pages, compromising the uniqueness of each page.
How to Fix it
To address the challenge of duplicate content, the initial step involves noindexing pages that don’t receive search engine traffic but contribute to the problem. Take, for instance, category filters generating unique URLs; this can be resolved by applying the noindex directive to those specific URLs.
Once you’ve successfully noindexed the necessary URLs, you can employ the canonical tag (“rel=canonical”). This tag signals to search engines that certain pages are duplicates or slight variations of the same page, prompting search engines to identify and handle them appropriately.
To distinguish between duplicate and original pages, leverage the canonical tag. Canonicalization serves a broader purpose than just resolving duplicate content; it also enhances the value of your backlinks. Multiple URLs linking to a single URL consolidates their impact.
Implementing canonical tags can be challenging, so we recommend seeking assistance from an SEO professional with technical expertise. If you prefer managing canonicals on your own, Google offers a helpful tutorial to guide you through the process.
After addressing technical issues, create original content for non-noindexed or non-canonical pages. While this can be time-consuming, especially for large ecommerce sites, it’s crucial for competing with Amazon on Google’s first page. To streamline the handling of duplicate content issues, use templates for product and category page descriptions to improve efficiency.
Thin Content
E-commerce sites often grapple with the persistent challenge of thin content as a common technical SEO issue. Even if you successfully address duplicate content problems, the presence of pages with insufficient content remains a concern.
It is critical to recognize that thin content has the ability to severely damage whole e-commerce SEO strategies. One example is eBay, which experienced a 33% decline in organic traffic due to a thin content-related Panda penalty.
However, instead of obsessing over the unpleasant features, we should shift our focus. Our data, gathered from an examination of 11 million Google search results, indicates an interesting trend: lengthier content consistently outranks its thinner counterparts.
Why it happens?
E-commerce sites frequently struggle with thin content, mainly because of the difficulty in creating distinct and meaningful information for identical items. The problem arises when attempting to provide unique descriptions for many products in the same category. Consider the following scenario: after covering one running shoe, the process appears to be repetitive for the next 25.
Despite this legitimate concern, it is crucial not to let it hinder content production. Aim for a minimum of 500 words on your critical category and product pages, with a maximum of 1000 words. This ensures that your website’s content maintains depth and quality, leading to a more robust online presence.
How To Fix It
Firstly, identify the pages on your site that lack substantial content. “Thin content” in this context refers to brief snippets that do not add distinct value.
To pinpoint such pages, you can either review each page individually or utilize a tool like Raven Tools, which categorizes pages with fewer than 250 words as having a “low word count.”
Once you’ve identified these pages with thin content, the next step is to enhance them with high-quality, original material. Using templates can significantly expedite this process.
Emphasizing the originality of your content is crucial. Actively engaging with the items you sell allows you to achieve true uniqueness. Share your thoughts, express your opinions, and capture images of your products. This approach will set your product descriptions apart for both users and search engines.
Site Speed
Google has said that site speed is an important component in their algorithm. It has a direct influence on your whole performance, not just ecommerce SEO. According to Radware’s research, poor load times can result in a 29.8% increase in shopping cart abandonment.
Why It Happens
E-commerce site pages often load slowly for three main reasons:
- Bloated E-commerce Platforms: Some e-commerce platforms inherently suffer from slow loading times due to their bloated code. Unlike platforms like WordPress, where you can enhance speed with a plugin, fixing this issue isn’t as straightforward.
- Large Image File Sizes: While high-resolution product images are excellent for customers, they can significantly slow down your page loading speed, akin to molasses in winter.
- Slow Hosting and Servers: The adage “you get what you pay for” holds true in web hosting. Opting for a sluggish hosting plan can put the brakes on your site’s maximum speed potential.
The good news is that addressing these site speed issues is relatively straightforward.
How to Fix it
Upgrade your hosting service, considering your specific preferences and needs, including support, cost, and security. Strive for a minimum monthly budget of $50 to ensure optimal performance, as choosing a lower budget may significantly impact your loading speed.
Furthermore, consider investing in a Content Delivery Network (CDN) as a cost-effective strategy to significantly improve your site’s loading speed. An additional advantage is the enhanced security against potential attacks and hacks that a CDN offers.
When it comes to ecommerce product pages, prioritize the optimization of image file sizes through compression. Make sure that your images are exported in a way that is optimized for the web to enhance overall performance.
E-Commerce SEO Best Practices
Navigating the realm of SEO for e-commerce presents a formidable task, given the sheer volume of online retail sites numbering in the tens of millions. Standing out in this crowded space is no walk in the park.
Despite the apparent challenge of boosting your SEO rankings, taking the first step towards improvement is well within reach. Start by adhering to the best practices we’re about to delve into.
If your e-commerce website hasn’t undergone any optimization, we strongly recommend following this guide sequentially. On the other hand, if you’ve optimized your site before, feel free to incorporate my advice according to your needs.
Now, let’s delve into the intricacies of SEO for e-commerce.
Conduct Keyword Research Effectively
Every e-commerce store owner should prioritize comprehensive keyword research for their store. Begin by identifying the most relevant and popular keywords in your niche. Then, delve into the customer intent associated with each term.
The goal of a search query is largely reflected in keyword intent. Analyze the specific terms people use when searching for a product online, along with the corresponding Google results, to pinpoint it.
There are two primary types of keyword intent that you’ll commonly encounter.
- Informational Keyword Intent
The first is Informational Keyword Intent. This occurs when consumers are seeking answers to queries or want to delve deeper into a topic to gain more knowledge. They are not actively looking to make a purchase at this time. For instance, if you operate an outdoor gear company, an informative keyword might be “best hikes near San Francisco.”
- Commercial Keyword Intent
Commercial Keyword Intent, on the other hand, arises when users actively seek information to facilitate a purchase. When a consumer has a specific product in mind but is uncertain about where to find it, they utilize commercial keyword intentions. This is evident when customers search for phrases such as “buy digital camera” or “find new laptop deals” on Google.
- Determining Keyword Intent
While determining keyword intent may seem challenging, there are methods to simplify the process. For instance, AgencyAnalytics recommends breaking it down into phases. Scrutinize search engine results pages (SERPs), paying special attention to sponsored advertisements, knowledge graph results, and organic listings.
When evaluating Google advertising for commercial intent, examine keyword bid prices to gauge keyword competitiveness. Additionally, assess your analytics and identify content with significant bounce rates, as this may indicate a misalignment with search intent.
Seeking assistance is vital for refining your site’s keyword mix. Let’s now look at several tools that might help you find SEO e-commerce keywords.
For SEO E-Commerce Research, Use Ubersuggest and AnswerThePublic
Google’s keyword planner is a good starting point, but if you’re aiming for a more thorough approach or need specialized assistance in expanding your keyword targets, consider exploring additional options. Let’s delve into some alternatives that can enhance your ability to develop target keywords for your e-commerce SEO strategy.
- Ubersuggest
Ubersuggest streamlines online keyword research. Just input a seed term like “digital marketing,” and the tool generates a range of related keywords along with comprehensive statistics. This data empowers you to select the most pertinent terms for your research.
The Ubersuggest interface is user-friendly and uncomplicated, catering to content writers, bloggers, copywriters, and marketers seeking fresh content ideas.
Moreover, Ubersuggest offers additional services like backlink analytics, rank tracking, and site audit reports, making it a valuable resource for individuals aiming to enhance their online presence and refine their content strategy.
- Backlink Data
Ubersuggest proves to be a valuable tool for evaluating the connections to your site as well as those of your competitors. Head to the Backlinks section and select the Backlink Discovery Tool.
Simply input a domain name, whether it’s yours or not, and Ubersuggest will present a comprehensive list of websites linked to it. This feature is particularly useful for identifying potential targets for link building.
- Rank Tracking
Ubersuggest’s rank tracking feature offers a comprehensive view of your organic Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) position for target keywords. It serves as an effective method for monitoring your progress over time, easily accessible from the Dashboard on the left side of the screen.
- Site Audit
Initiate a site audit to uncover any issues that might be impacting user experience and organic traffic. Consider the audit a fundamental step and establish a routine of checking it regularly to address any identified issues promptly. The Site Audit tool is conveniently located in its own tab on the left-hand sidebar.
Once the audit is complete, it will pinpoint your primary SEO challenges and provide specific recommendations on how to address them.
- Answer the Public
Answer the Public, a sophisticated search listening tool that utilizes Google autocomplete data, has recently been acquired by NP Digital. This program stands out for its ability to generate a plethora of questions for any phrase you input, making it particularly valuable for identifying long-tail keywords.
Using Answer the Public is straightforward. Just input your keyword on the homepage, and the platform will display a comprehensive list of related queries organized under various topics such as where, when, how, and what. The questions are conveniently arranged in alphabetical order, and you can download them as a .csv file. While the basic features are free, there is a subscription plan available for individuals seeking enhanced functionality. As an illustration, let’s consider the term “multivitamins.”
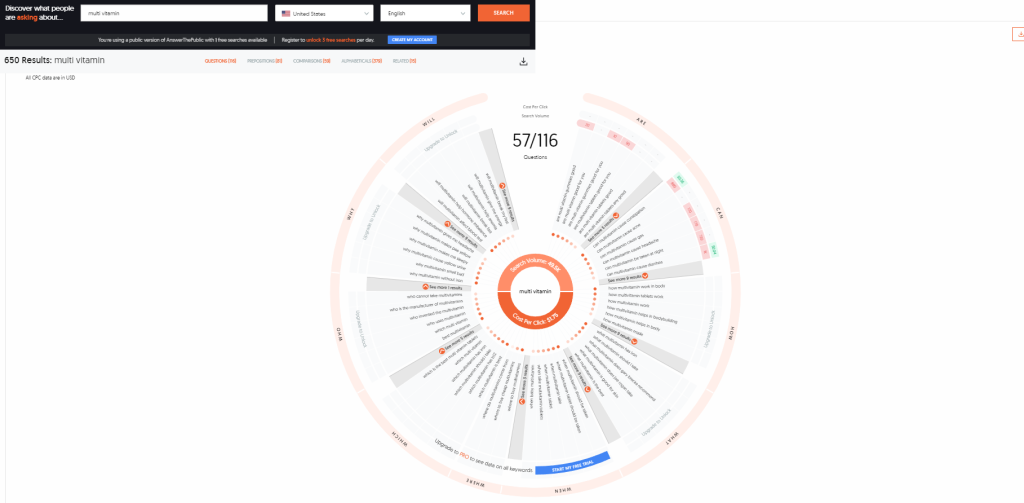
Analyzing the results provides a more nuanced understanding of the questions people are asking, along with valuable insights into their intent. With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive data, this tool proves to be a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their keyword research efforts.
Optimize Product Pages for Better Ranking
To enhance search traffic and attract potential customers, every business owner must optimize their website’s on-page features. On-page SEO encompasses elements such as site structure, meta descriptions, and header tags.
However, not every on-page element on an e-commerce site requires optimization. Let’s focus on what is most crucial for online retailers: product descriptions, photos, and reviews.
- Optimizing Your Product Descriptions:
Product descriptions play a vital role as they provide essential, keyword-rich information that Google utilizes for ranking. Additionally, these descriptions serve as persuasive tools, enticing consumers to make a purchase.
When optimizing product pages, keep three key aspects in mind:
- Identify the critical elements on the page.
- Determine how to maximize visibility and impact with these elements.
- Use this information to enhance the effectiveness of your product descriptions.
Consider implementing the following actions:
- Adding multiple, high-quality, unique images
- Incorporating relevant keywords
- Providing detailed, keyword-rich descriptions
- Including compelling calls to action (CTAs)
- Adding testimonials
These suggestions go beyond conventional product descriptions, emphasizing the significance of user reviews and effective CTAs.
- Optimize Your Images
Optimizing images is often an overlooked aspect of on-page SEO for e-commerce. While images are excellent for conveying a message, having too many can distract from your intended communication. Ensure the use of high-quality images and optimize them for SEO to improve search engine rankings and attract more traffic.
Here are some tips for optimizing images:
- Provide captions with alt tags.
- Keep images as small as possible without compromising quality.
- Use keywords in file names.
Feature Reviews
Reviews provide valuable insights for shoppers and help build trust with potential customers, ultimately enhancing conversion rates. Encourage customers to leave reviews through automated messages or email campaigns.
Before we move on, consider these additional on-page optimization tips:
- Use canonical tags to link duplicate product pages.
- Create a well-written page with essential product information, images, and videos.
- Include at least one clear call to action (CTA) on your product page.
- Clearly state shipping details and policies upfront.
Implementing these strategies collectively contributes to a comprehensive approach for enhancing e-commerce SEO and driving business growth.
Make Sure Your Site Is User-Friendly
Ensuring a top-notch user experience (UX) is paramount for e-commerce stores. It’s not just about aesthetics; it’s about functionality. UX encompasses the entire spectrum—from seamless navigation to the overall site “feel.” It’s about aiding users in finding what they seek, maintaining engagement, and delivering the best possible experience.
Don’t overlook the importance of user experience in SEO. Your rating is closely related to the user experience. Google, for example, assesses user experience using Core Web Vitals, focusing on three main areas:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Google gauges a page’s usefulness based on the load time of its most significant visible elements.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures how much interactive elements move post full-page load, ensuring a stable user interface.
- First Input Delay (FID): It gauges how swiftly a page responds to user input.
As a site owner, optimizing Core Web Vitals involves several actions:
- Enhance Site Load Time: Speed matters. Users, and Google, appreciate a fast-loading site.
- Manage Ads Effectively: Ensure ads don’t disrupt the user experience. They should seamlessly integrate without causing interference.
- Create an Interactive Site with Clear CTAs: Foster an interactive environment with clear Calls to Action (CTAs). Guide users through your site effortlessly.
Don’t Forget Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords, in essence, are more detailed and specific search phrases, typically comprising at least three words. Despite their low search volumes, these phrases hold significant value for e-commerce stores. Although they generate less traffic, they often result in remarkably high conversion rates, making them a lucrative asset.
Long-tail keywords prove beneficial for any business, especially in highly competitive areas.
To discover these phrases, consider using Google’s “People Also Ask” function or a keyword tool like Ubersuggest.
Navigate to Ubersuggest’s Keyword Ideas tab, accessible under the Keyword Research header. As an example, let’s take the seed keyword “camping gear.” The program will then generate a comprehensive list of similar terms.
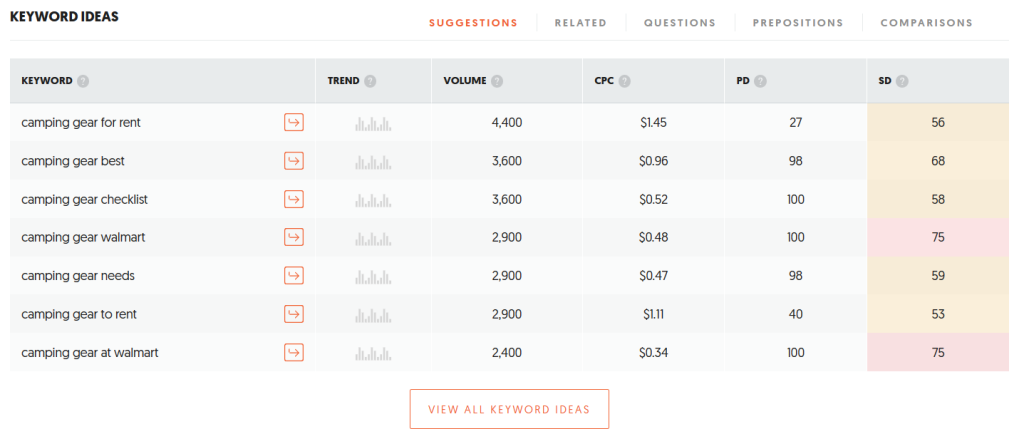
Due to the lower competition levels associated with long-tail keywords, it’s advisable to set the SEO Difficulty filter to ‘easy’ for the best results.
Use a Simple URL Structure
Having a straightforward URL structure is crucial for an improved user experience and better SEO in the realm of e-commerce. When your e-commerce site adopts a simple URL structure, sharing products across social media and other platforms becomes notably easier. To achieve optimal results, prioritize URLs that are highly readable.
Let’s consider an example of what you should avoid:
https://www.example.com/articlesabouthiking/.
A much more effective approach would be utilizing a URL like https://www.example.com/hiking-articles.
For additional guidance, Google offers advice on enhancing URL structures. Now, let’s delve into some practical tactics for improving your URL structure:
- Incorporate Keywords: Before deciding on a URL structure, consider important keywords. Search engines crawl your URLs, making keyword inclusion a critical ranking element. For example, if “mens sneakers” is a frequently searched word, using it in the URL of your category page might help it rank higher.
- Avoid Stop Words: Steer clear of common stop words such as “the,” “and,” “of,” and “a.” These words hinder the readability of your URL and may negatively affect your SEO rankings. Eliminate them from your URLs. For instance, transform a URL like http://example.com/what-are-the-best-hiking-shoes to http://example.com/best-hiking-shoes.
- Implement Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs are a useful navigational feature that allows users to retrace their travels and return to the beginning place. Breadcrumbs provide extra SEO benefits in addition to improving usability. For example, if a visitor navigates from the main site to a blog article, the breadcrumb may be “Home > Blog > This Post.” Breadcrumbs may be readily integrated into numerous web design tools by utilizing markup elements or JavaScript.
Use Schema Markups to Help Google and Users Understand Content
Schema markups serve as HTML tags providing additional information to search bots regarding webpage content. This, in turn, enhances your SEO efforts for e-commerce.
Implementing schema markup provides rich snippets, allowing search engines to prominently display more extensive information about individual queries in search results. This assists people in swiftly locating what they need by presenting various forms of information.
Product markup snippets, audio snippets, and review snippets are examples of rich snippets.
Now, let’s explore the various e-commerce schema types:
- Product Schema:
- An extension for products, services, and organizations.
- Facilitates the discovery of new products and services in web search queries.
- Provides rich product information such as images, price, and availability.
- Enables the display of product ads on SERPs.
- Review Schema:
- Enables online reviews.
- Utilizes author and title filters for locating specific reviewers on your website.
- Helps searchers find product reviews effectively.
- Product Availability Schema:
- Comprises a list of available products for purchase.
- Can exist as a single page or within an online store.
- Details include product name, description, price, images, and variants.
- Video Schema:
- Metadata describing content and format.
- Includes details like audio language, video resolution, or age rating.
- Price Schema:
- Technique for pricing products or establishing a price range.
- FAQ Schema:
- Markup to add a list of questions and answers to a page.
- An example can be found in the FAQs section at the bottom of this post.
Content Matters for E-Commerce
In e-commerce, success extends beyond visuals and keywords. Your SEO strategy should encompass written content. Regularly publishing relevant material not only draws in organic traffic but also fosters trust, enhances website rankings, and establishes authority in your niche.
Diversify your approach by considering various content types:
- Craft how-to guides and address frequently asked questions.
- Highlight new product launches and any noteworthy developments.
- Develop a glossary page for industry-specific terms.
- Incorporate user-generated content (UGC) to engage your audience.
- Showcase testimonials and successful product launches.
- Utilize video demonstrations and Q&A sessions.
- Host webinars to provide valuable insights.
To generate more ideas, delve deeper into understanding your audience. Recognize their concerns and problems to tailor your content and offer solutions.
Now that you’re acquainted with content types, let’s explore how to construct a robust content strategy catering to your audience:
- Understand Your Customers: Create buyer personas to better understand your target customer.
- Identify Preferred Content: Examine your content data to find the most popular categories. Conduct surveys or focus groups to learn about customer preferences.
- Make a Content Calendar: Develop a content development timetable.
- Tailor Content for the Buying Cycle: Ensure your material is relevant at each point of the purchase cycle.
- A/B Testing: Use A/B testing to experiment with essential components such as titles.
- Measure and Adjust: Monitor findings and make changes as required.
Avoid Duplicate Pages And Content
Have you ever found yourself on a website where everything seems oddly familiar? This is a common issue, particularly with product and category descriptions on online retail sites that heavily rely on catalog material and photographs.
The reason behind the frequent reuse of the same descriptions by e-commerce vendors is often a lack of resources to create new content. Even if time constraints prevent a complete rewrite, there are practical steps you can take to significantly minimize duplication across your site, especially in critical areas like product descriptions.
Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Utilize a CMS with site-wide 301 redirects or implement canonical tags on pages prone to duplication. This is particularly useful for pages with similar names or URLs.
- Add a suffix to the URL. This simple adjustment can help differentiate pages and reduce the appearance of duplication.
- Incorporate various product photos. Diversifying the visual content helps break the monotony and enhances the uniqueness of each product.
- Include distinct keywords on different pages. Tailoring keywords to specific pages can contribute to making each page stand out and be more search-engine-friendly.
Prevent Page Speed From Lowering Your Ranking
The time it takes for a web page to load is critical for user experience. Page speed is a crucial factor in website rankings, and numerous surveys consistently reveal that users are intolerant of delays when waiting for a site to load. According to a recent survey, 19% of buyers would abandon a website that takes more than two to three seconds to load.
Web users prefer sites that load in less than two seconds, but faster loading speeds are always appreciated. You can utilize tools like Cloudflare or Google’s testing tool to assess your current page speed.
If your website is too slow, the first step is to identify the cause. It could be due to an overload of content for your server to handle, too many applications slowing download speeds, slow-loading graphics, or issues with your web host. While achieving a perfect 100% score on Google’s PageSpeed Insights may be unrealistic for many e-commerce sites, there are steps you can take to enhance load times:
- Reduce the number of images on your pages.
- Compress files to reduce their size.
- Minimize the use of social media widgets.
- Optimize your images for faster loading.
- Maintain a clean layout with ample white space.
- Limit redirects and HTTP requests.
- Improve your server response time.
If these measures prove insufficient, consider switching web hosts or upgrading your hosting package to better align with the demands of your site.
Link Building For E-Commerce
Building links is crucial for SEO as it directly impacts your website’s rating. High-quality links signal to Google that your site is reliable, playing a pivotal role in determining its ranking for specific keywords.
The question then arises: How do you go about creating these vital backlinks? Here are various approaches:
- Internal Backlinks: Strategically link within your own content.
- Guest Posts: Contribute articles to other websites in your niche.
- Social Media Ads: Utilize paid ads on social media platforms.
- Content Sharing on Social Media: Regularly share your content across various social media channels.
- Press Releases: Issue press releases to gain exposure.
- Blog Comments and Forum Participation: Engage in relevant discussions and share your insights.
- Infographics Creation and Sharing: Develop visually appealing infographics and share them online.
- Whitepapers and Case Studies: Publish in-depth whitepapers and case studies.
While these methods may require time and effort, it is crucial to emphasize that shortcuts, such as buying links, are not recommended. Purchasing links goes against Google’s policies. Moreover, cheap links often compromise quality, leading to lower SERP ranks, reduced traffic, and significant damage to your site’s reputation. For sustainable and positive SEO outcomes, it is imperative to build quality links through legitimate channels.
Make Social Sharing Easy
Google’s Matt Cutts once stated that social sharing had no direct influence on SEO; however, there is a divergence of opinions on this matter. While social media sharing may not have a direct impact on SEO metrics, it plays a crucial role in increasing brand recognition and promoting your firm.
Moreover, the frequency of social media mentions can significantly influence your SEO by:
- Increasing organic traffic and visibility.
- Enhancing local SEO efforts.
- Expanding the reach of your content and strengthening brand recognition.
- Creating valuable backlinks.
Consider using tools like Buffer or Hootsuite to streamline your social media sharing process. These platforms allow you to schedule and broadcast content from your website across all your social media profiles automatically.
25 Additional Quick Tips For E-Commerce SEO
Ensure that you’ve addressed every aspect of SEO optimization for your online business. Keep up the good work! There are several tactics that will undoubtedly boost your organic traffic and revenue. Take a look at these 25 tips briefly:
Verify Your SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate is essential for your online business. It not only adds “https://” before your URL but also enhances your SEO, instills confidence in Google, and safeguards consumer data.
Enhance Meta Descriptions
Craft compelling meta descriptions to increase organic search engine click-through rates (CTRs). While it may not directly impact rankings, a higher CTR can have a significant influence. Employ phrases like “buy online” to convey product availability before consumers even click, as many e-commerce sites do.
301 Redirect Out-of-Date Products
When dealing with expired or discontinued items, use a 301 redirect to a more recent product page. This ensures the transfer of all SEO value to the updated page, potentially resulting in a boost in rankings.
Elevate Category Pages
Treat category-based pages (such as those for men or women) as separate homepages with distinct content and keywords. Organizing these pages based on specific keywords, like “men’s basketball shoes,” can contribute to higher rankings.
Implement Category-Level Navigation
Maintain category-level navigation on your e-commerce store. This makes your website more accessible for Google to crawl and facilitates user navigation, enhancing both visibility and sales.
Enhance Your Online Store’s Visibility
Ensure robust SEO for your marketplace—did you know that 38% of e-commerce product searches originate on Amazon? Consequently, make certain that your product is featured and includes a backlink directing to your website. In just ten minutes of optimizing for Amazon, one shop experienced a remarkable 320% surge in sales.
Craft a Perfect Title Tag
To capture user attention, create a title tag that spans 60 to 70 characters, consistently incorporating the relevant keyword. Users are more likely to click if the tag is intriguing. Always include the product name in your meta titles to precisely match what the searcher is seeking.
Revamp Your 404 Page
Transform your 404 error pages into revenue-generating tools. Utilize Google Search Console to identify 404 error pages and promptly implement 301 redirects to the most relevant pages on your website, preventing missed sales opportunities. You can also personalize your 404 error message to guide visitors to your online store’s preferred pages.
Integrate Live Chat
The addition of live chat to your website alone can boost conversion rates by over 50%. This allows consumers to contact support instantly, avoiding the wait for phone or email responses. Live chat provides immediate access to customer support agents, aiding customers in making well-informed purchasing decisions.
Boost Internal Links
Increase internal linking to reduce your website’s bounce rate. This not only improves your rating but also ensures that customers stay on your store for a longer duration. Utilize internal links to suggest related products or items purchased by other visitors, enhancing your website’s structure and encouraging more relevant purchases.
Diversify Your Anchor Text
For targeted searches, use keywords in anchor text instead of generic phrases like “click here” to enhance page rankings. This practice may also prompt customers to click through more often.
Optimize Your CTAs
Regularly update your website’s calls to action, optimizing them for specific sales, holidays, and promotions to observe an uptick in conversion rates.
Establish Credibility With An About Us Page
Crafting an “About Us” page provides Google with more context about your business and offerings while instilling confidence in your shop among customers.
Include Product Suggestions
Commence selling immediately upon landing on your homepage by recommending popular items to reduce bounce rates and swiftly capture consumer attention.
Optimize Out-of-Stock Page Content
During out-of-stock situations, collect leads from product pages. Instead of leaving the page blank, which may prompt users to exit, request their email addresses in exchange for stocking notifications.
Ensure Proper Heading Structure
Check that the appropriate header tags are on your product pages. Use the product name as the H1 header tag and employ H2s for headers related to refunds, shipping details, and product descriptions to enhance readability and search engine optimization.
Instill A Sense Of Urgency
Include a sense of urgency in your product pages and meta descriptions for organic search. Create a feeling of urgency using countdowns to persuade viewers to make purchases, similar to successful Kickstarter projects.
Boost Traffic through Product Comparisons
Create SEO content by writing “versus” type blogs that compare popular items, increasing organic traffic to your website.
Craft Gift Guides
Develop holiday gift guides to boost organic traffic. Gift guides help customers find the ideal product, targeting high-intent commercial keywords and increasing traffic and conversion rates.
Incorporate Video Content
Prefer video content for product demos, as it builds confidence in consumers. Video content is particularly crucial for businesses offering toys, DIY equipment, or consumer electronics.
Utilize Paid Search
Paid search is a powerful tool for raising brand awareness and encouraging natural sales. Bid on branded PPC phrases to dominate organic results for your business, ensuring every organic search results in a click through to your website.
Engage In Blogger Outreach
Request product reviews from well-known bloggers in your product sector to obtain links in roundup-style posts quickly.
Establish An Affiliate Program
Launch an affiliate network to incentivize bloggers to promote your goods on their websites, strengthening your website’s authority and increasing rankings and revenues.
Leverage Search Console For Opportunities
Use Search Console to identify keywords you’re inadvertently ranking for and create dedicated pages to drive traffic. Additionally, use Google’s Ads Keyword Planner to find high-intent, purchase-based keywords contributing to organic sales.
Install An SEO Plugin
Install the Yoast SEO Plugin for WordPress to address missed on-page SEO tasks. Use ScreamingFrog to crawl your site for 404 errors, duplicate content, and other issues.
5 eCommerce SEO Mistakes Making Your Website Bloat
It is crucial to optimize your eCommerce website to ensure swift and efficient crawling by search engines, facilitating better understanding. Frequently, we come across common challenges on eCommerce sites that can be promptly addressed, helping to maintain your site devoid of unnecessary, non-indexable, and duplicate pages.
By tackling these five prevalent issues, you will empower search engines to focus on the specific pages you aim to rank.
Mistake #1: Linking To Canonical Product Pages
Many eCommerce websites automatically include the product category in their URLs, a default setting in popular CMS platforms. Consider the following example:
Product: 55-inch Smart TV
- Simple URL: example.com/55-inch-smart-tv
- Category URL 1: example.com/televisions/55-inch-smart-tv
- Category URL 2: example.com/electronics/55-inch-smart-tv
- Category URL 3: example.com/smart-home/55-inch-smart-tv
While multiple-category URLs normally canonicalize back to the basic product URL (always double-check for the canonical link), it still generates superfluous crawling URLs when only one is required.
For an entire product range on an eCommerce site, this leads to thousands of unnecessary crawled URLs. Fortunately, most CMSs offer the option to use the simple product URL instead of those with the category path. This choice streamlines the website significantly, providing both a more efficient structure and internal linking advantages by directly linking to the canonical URL without relying on canonicals for value transfer.
Mistake #2: Keeping Outdated Pages Live
Out-of-stock (OOS) management is crucial for eCommerce websites to ensure a positive customer experience and successful search engine optimization. As your product line evolves, having a solid plan for handling discontinued or out-of-stock items becomes essential to prevent consumer frustration and maintain site efficiency.
Over time, the accumulation of discontinued or out-of-stock product pages can pose challenges. Imagine customers stumbling upon these pages through search engines or your own website – not an ideal scenario. Additionally, this buildup may lead to an unnecessary increase in indexed and crawled pages. Therefore, having a systematic approach tailored to your specific product range, website, and industry is imperative.
Here’s a practical OOS strategy to consider:
Discontinued Products:
- Keep pages for discontinued products with high search volume live. Provide alternatives or include an email sign-up form on the page.
- For discontinued products with low search volume, consider moving them to a related category, especially if they have referring URLs. Alternatively, allow them to redirect to a 404/410 error page.
- Streamline your site by removing internal links related to discontinued products.
Out-of-Stock Products:
- If an out-of-stock product is expected to return soon, maintain the page as is or enhance it by suggesting similar products and/or including an email sign-up form.
- For items permanently or semi-permanently out of stock, opt for a 301 or 302 redirect to a relevant category page. Remove internal links to these items to prevent unintentional customer landings.
Implementing this strategic framework will not only enhance the user experience but also contribute to maintaining a streamlined and search engine-optimized website. Remember that the specifics of your strategy should align with the nature of your items, the features of your site, and the expectations of your business.
Mistake #3: Legacy Redirects And 404s
Addressing issues such as obsolete product pages, internal redirects, and 404 failures that may still be connected internally is crucial for ensuring the efficiency of your e-commerce site. These issues accumulate over time and can have a negative impact on the site’s user experience and search engine navigation.
Examining your e-commerce site for internal linking to redirects is vital. This not only hinders search engine crawlers but also slows down page loading speeds, leading to higher bounce rates and lower conversion rates. Essentially, it contributes to the overall bloating of your website.
It is critical to identify and rectify 404 issues promptly. This ensures a continuous journey for search engine crawlers and a seamless experience for consumers, eliminating dead ends. Redirecting historical 404s and updating internal links helps keep search engines focused on high-ranking pages, encouraging customer conversions.
Utilize Lumar (formerly Deepcrawl) to efficiently identify 301 redirects and 404 errors at scale. Crawling your site and utilizing the non-200 page overview provides insights before delving into the 301 redirect and broken pages report. This step-by-step process helps pinpoint affected pages and sources, enabling targeted actions to enhance site performance.
Mistake #4: Filters Generating Crawlable Parameter URLs
When a website features a multitude of parameterized pages, often due to the incorporation of filters and facets, it imposes a substantial burden on search engines during the crawling process. If these parameter pages are not properly designed, they closely resemble category pages, offering minimal value to search engines. It is crucial that these pages do not attain ranking status or compete with our primary categories.
To successfully prohibit search engines from scanning these less valuable pages, a two-pronged strategy is proposed: either disable parameterized filters in the robots.txt file or apply a “nofollow” tag to internal links leading to these pages (or consider adopting both tactics). This ensures that certain pages are not visible to search engines. If you want to remove them from the index, initiate the process using a “noindex” tag.
Consider this: If you’re using facets for indexing to capture more search words, a comprehensive assessment is required to ensure that relevant targeted parameter pages may still be scanned efficiently. This allows for a balanced approach to optimizing search performance while maintaining control over crawlable information.
Mistake #5: Links Injected by JavaScript
Many eCommerce businesses heavily depend on JavaScript to enhance the functionality of their websites. JS apps, plugins, and extensions can significantly enhance the overall user experience on an e-commerce site.
Conducting a thorough analysis of a website by crawling it with and without JavaScript rendering is crucial. This helps in comprehending the URLs generated during the rendering process. The rendered Domain Object Model often includes URLs not present in the HTML, which may be overlooked in a typical crawl without JavaScript.
Search engines encounter these URLs while displaying pages, enabling them to be crawled and indexed. However, many of these URLs may lack significance, being repetitions, parameterized sites, or pages with minimal ranking relevance.
Identifying these URLs is essential, and appropriate actions should be taken. They should either be removed from the Domain Object Model or marked as “nofollow” or “noindex” to prevent them from contributing unwanted URLs to the crawl and indexing processes of search engines. This is crucial for optimizing resources and avoiding undue strain on the rendering budget.
Conclusion
A technical SEO audit can be a lot of work for an eCommerce company to undertake, what with Google Search Console, crawlability, site architecture, on-page SEO, and page enhancements. These audits are extensive and require a significant amount of time and energy to complete correctly. SEO tools can point you in the right direction, but they cannot always provide specific solutions for your company’s goals and nuances. That is why we always recommend conducting a custom audit, whether on your own or with the assistance of an experienced company like PageTraffic.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is ecommerce technical SEO audit important?
Technical SEO audits and strategies are important because they ensure that your website is easy to navigate and free of technical issues that prevent it from ranking in search engines. To attract organic traffic, you must use technical SEO.
What is technical SEO for a website?
Technical SEO is the process of enhancing the technical features of a website in order to boost its search engine rankings. Increasing a website’s speed, crawlability, and search engine readability are the foundations of technical optimization.
What is the difference between technical SEO and content SEO?
Technical SEO, in a nutshell, refers to improving the technical aspects of your website, such as site speed and loading errors. Content SEO is the process of improving the content on your website’s pages, such as blog posts. Both SEO strategies aid in the visibility of your website in Google search results.